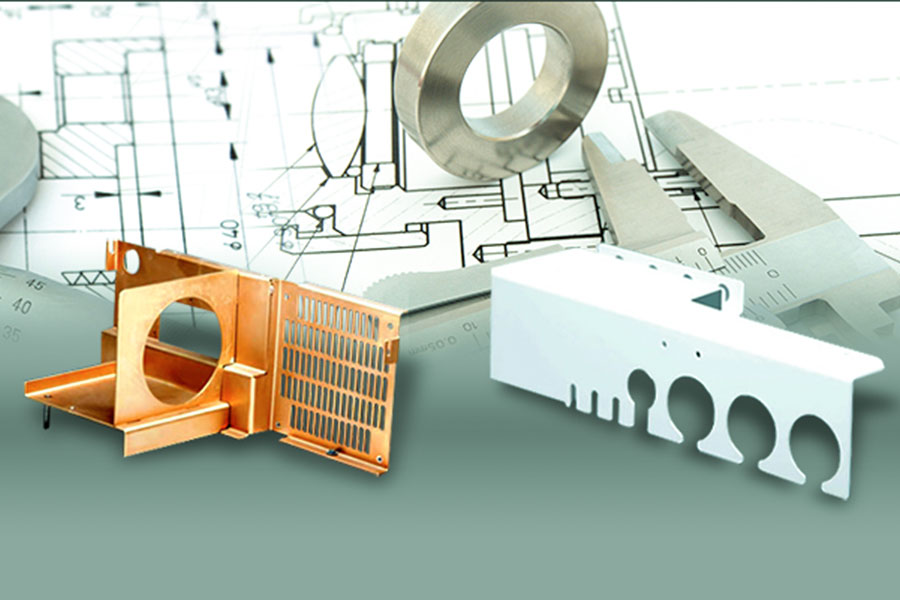
판금 제작은 절단을 통해 금속 시트를 기능 구성 요소로 변환하는 핵심 제조 기술입니다. 자료 선택은 제품의 성능, 비용 및 응용 프로그램 시나리오를 직접 결정합니다. 아연 도금 판금, 알루미늄 판금 및 스테인리스 스틸은 3 가지 주요 기판입니다. 아연 도금 판금 표면 아연 층은 효과적인 방지 방지, 강도 및 경제를 통해 가정 기기 및 자동차 산업에서 널리 사용됩니다. 알루미늄 판금 은 경량, 부식성 및 높은 열전도율의 장점을 가지고 있으며 항공 우주 및 전자 제품에 선호되는 라디에이터가되었습니다. 반면, 스테인레스 스틸은 고온과 내식성으로 인해 화학 장비 및 의료 기기에서 우세합니다.
또한 구리 및 티타늄 합금과 같은 특수 재료는 전도도, 강도 또는 생체 적합성과 같은 특정 요구에 대해 다른 특성을 제공합니다. 벤딩 프로세스 매개 변수의 합리적인 선택 및 일치는 판금 부품의 기능과 경제를 보장하기위한 핵심 전제 조건입니다.
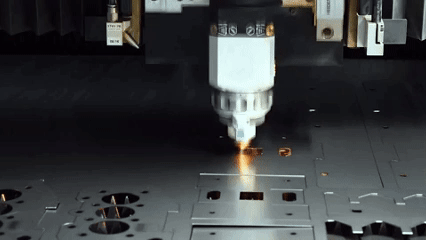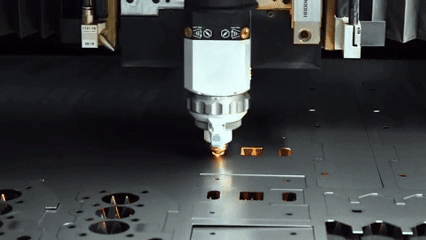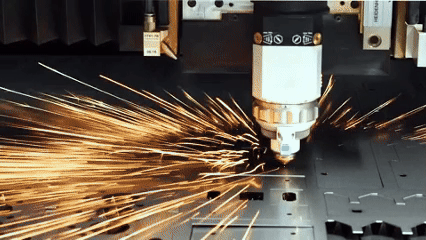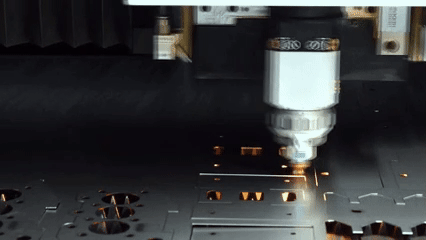
판금 제조 란 무엇입니까?
절단 과정은 재료의 초기 모양을 결정합니다. 어셈블리의 기능과 안정성을 보장하기 위해 연결 또는 용접을 볼트. 소규모 배치 사용자 정의의 유연성으로 인해 빠른 반복 또는 복잡한 형상이 필요한 응용 프로그램 시나리오에 특히 적합합니다. href = "https://jsrpm.com/sheet-metal-fabrication"> 곰팡이 설계 최적화 , 자동화 장비 적용 및 엄격한 품질 검사 수행, 판금 처리는 정밀도와 비용의 균형을 맞출 수 있으며 현대 제조에서 필수적인 기초 기술 중 하나가 될 수 있습니다.
판금 제조에 일반적으로 사용되는 재료는 무엇입니까?
1. galvanized phethe metal
표면 아연 도금 층, 우수한 녹 예방 능력, 고비용 성능. 환경은 냉장고, 에어컨 , 건물 울타리, 지붕 및 자동차 섀시입니다.
.2. 알루미늄 판금
가볍고 강력하며 부식에 대한 저항력, 전기 전도성이 우수한 것으로 알려져 있습니다 (신체 성분), 전기 부류 (방열판, 전화 싱크, 전화기) 팩).
3. 스테인리스 스틸 판금
크롬 합금은 고온, 산 및 알칼리 부식에 대한 저항의 특성을 갖는다. 화학 장비, 의료 기기 , 주방기구 및 고급 장식 엔지니어링에 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
.4. Copper 합금 판금
뛰어난 전도도, 열 전도도 및 항균 특성, 주로 전기 접촉기, 냉장 파이프, 데코레이션 및 고급 위성 장비에 사용됩니다.
.5. 티타늄 판금
고강도, 중량비, 부식성, 우수한 생체 적합성, 항공 우주, 고급 스포츠 장비, 의료 임플란트 및 기타 가혹한 환경에 적합합니다.
. 
아연 도금 강철 금속의 장점과 단점은 무엇입니까?
1. Excellent Rust Prevention Performance
galvanized 강철의 표면에서 아연 코팅 <"span class " Data-TranslateID = "CF7880B7FB6DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD5"0 "DATA-LEN ="189 "DATA-V-7B79C893 =" "> 금속 는 산소와 습기를 효과적으로 모욕 할 수 있습니다 (일반적으로 15-30). 또는 부식성 환경 (예 : 건물 지붕, 자동 구성 요소 등).
2. good 형성성 및 처리 성
시트 금속 굽힘과 같은 콜드 머시닝 기술 , gallvanized steel Metal 은 연소성이 높고 복잡한 모양으로 처리하기가 쉽습니다. 껍질을 벗기고 표면 보호를 유지합니다.
3. 경제 및 실용성
Galvanized steel Metal 은 스테인리스 스틸과 같은 고급 재료보다 비용이 낮고 유지 보수가 낮아서
아연 도금 강철 금속은 지속 가능한 개발의 요구를 충족시키기 위해 여러 번 재활용 할 수 있습니다. 재활용 과정에서 자원 폐기물을 줄이기 위해 아연 도금 시트를 재사용 할 수 있습니다.
1. 높은 초기 비용
아연 도금 프로세스는 강판의 생산 비용을 증가시키고 짧은 기간 동안 만 사용하는 경우 비용 효율성이 낮을 수 있습니다.
.2. 제한이있는 deal
판금 굽힘 중에 굽힘 반경이 너무 작거나 작동하지 않는 경우, Galvanized가 끊어 질 수 있습니다. 독성 가스가 생성되므로 용접 품질에 영향을 미치기 위해 보호 조치를 취해야합니다.
3. 아연 층 마모 위험
장기 마찰 또는 긁힘은 아연 코팅의 부분적 손실, 방 해부 효과 손실, 보호가 취약한 영역에서 추가되어야합니다.
.4. long-term Maintenance Cost
초기 비용은 낮지 만 마모를 정기적으로 검사하고 아연을 대체하고 적용하십시오. High.
5. 환경 분쟁
아연 폐기물 가스 또는 슬래그는 아연 도금 중에 생성 될 수 있습니다.
알루미늄 스틸 금속 굽힘의 균열을 방지하는 방법?
< "> 자료의 세 가지 측면에서 취해야합니다. 다음 :
<테이블 스타일 = "Border-Collapse; 붕괴; 너비 : 100.191%; 경계-넓이 : 1px; 경계 색상 : #000000; 높이 : 461.312px;" Border = "1">- 플라스틱 변형 능력과 정밀도 형성 사이의 균형은 핵심 모순 aluminum 판금 .
- 파열 위험 : 하드 알루미늄 플레이트 (H State)> 반-하드 (H32)> 어닐링 상태 (o State).
- 권장 솔루션 : 어닐링 알루미늄 플레이트+세그먼트 벤딩+윤활제 보조는 크래킹 속도를 <5%로 줄이기위한+윤활제 지원 입니다.
JS Company의 기술 데모
사례 : 새로운 에너지 차량 배터리 팩 브래킷 굽힘 엔지니어링.
챌린지 : 복잡한 다중 방향 굽힘 직렬 알루미늄 (1.5 mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm aluminum). ≥150mpa.
js scheme :
- 어닐링 및 노화를 통한 재료 특성 최적화.
- 사용자 정의 비대칭 다이를 달성하려면 r = 3mm 정밀도 굽힘.
- 세그먼트 굽힘 프로세스 채택 (최종 굽힘 전 90 °에서 사전 벤딩).
- 결과 : 수율은 72%에서 96%로 증가했으며 생산주기는 40% 감소했습니다.
wrap ""no-wrap " src = "https://www.jsrpm.com/webSite_img/i/2025/04/14/p7kd51-2.jpg"alt = "굽힘 기술의 다른 형태"너비 = "900"높이 = "600">
레이저 절단에서 금속 금속의 정확도를 제어하는 방법?
2. 인텔리전트 소프트웨어 지원
- cad/cam 통합 시스템은 절단 경로를 최적화하고 열 변형의 영향을 줄이는 데 사용됩니다.
- JS Company는 엔지니어링 팀이 특수 소프트웨어를 사용하여 스틸 플레이트의 응력 분포를 분석하고 변형을 보상하기 위해 미리 절단 매개 변수를 조정한다고 강조했습니다.
- 레이저 전력의 동적 조정, 절단 속도 및 보조 가스 압력 (예 : 산소, 질소 등), 재료에 따라 절단 효율 및 단면성, 구리 등의 균형을 유지합니다. 두께.
- js 사례 연구는 의 A Process Parameter의 범위에서 제어 될 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 재료.
2. 초점 위치의 진실 시간 정렬
1. 플레이트의 플랫 니스는 보장됩니다
JS company adopts a vacuum adsorption platform to fix sheet metal, with high precision rolling equipment for pretreatment, eliminating wavy deformation of sheet metal, ensuring that the surface of the cut is less than 0.02mm/m² of the flatness error.
2.Surface cleaning and oxide layer control
Ultrasonic cleaning is used to remove oil stains and impurities before cutting to prevent slag adhesion from affecting accuracy. For materials with high reflectivity, such as aluminum alloys, a special coating is used to reduce reflectivity.
Quality inspection and feedback mechanism
1.Online detection system
Integrated laser displacement sensor and CCD camera, real-time monitoring of cutting edge quality, automatic removal of defective products, proposed process optimization.
JS Company's Quality Control Process
- Samples from 3D contour scanner are provided to compare the deviation values between the design model and the actual cutting parts, and a detailed accuracy analysis is published (for example, an aeronautical aviation component the flatness error of only 0.003mm in the case of a customer).
- Establish a three-level quality inspection system for order repetition, including first inspection, process inspection and finished product inspection to ensure batch consistency.
Environmental and sustainable development control
The influence of ambient temperature and humidity changes on material size stability is reduced through constant temperature and humidity workshops (temperature ±2°C, humidity 40-60% RH).
My company reminds you that its green manufacturing processes, such as waste recycling system, not only reduce energy consumption, but also indirectly improve processing accuracy by reducing material waste (material utilization rate increases to over 92%).
Can carbon steel and aluminum steel metal be directly welded?
In sheet metal fabrication, the direct welding of stainless steel and aluminum plates faces great challenges, mainly due to their different physical and chemical properties:
Difficulties with direct welding
1.Formation intermetallic compounds
When stainless steel (e.g. 304, 316) comes into contact with aluminum (e.g. 1060, 5052) at high temperatures, iron reacts with aluminum to form brittle intermetallic compounds, leading to lower weld strength and even cracking.
2.Differences in thermal expansion coefficients
The thermal expansion coefficient of aluminium (about 23×10-6°C) is 1.4 times that of stainless steel (about 17×10-6°C) and is prone to deformation or cracking during welding due to thermal stress.
3.Differences in melting point and thermal conductivity
The melting point of aluminum (660 °C) is much lower than that of stainless steel (1375-1530 °C), and aluminum has a the thermal conductivity three times that of steel, which results in rapid heat loss during welding and makes it difficult to maintain the stability of the melting pool.
Feasible processes and limitations
1.Traditional arc welding (e.g. TIG/MIG)
- Feasibility: Special welding wire (e.g. ER4043 Al Si) are required and protective gases (argon+helium mixed gas) are added, but the weld strength is relatively low (only 50-70% of the base metal).
- Constraints: Porosity and slag inclusion are easily generated, and intermetallic compounds may expand during long-term use, leading to failure.
2.Brazing or diffusion welding
- Brazing: Low temperature brazing materials (e.g. Al-Si series) are used to fill gaps through capillary action, avoiding direct melting of the substrate, but joint strength is limited (usually<150MPa).
- Diffusion welding: It requires vacuum or inert gas environment to connect atoms horizontally at high temperature and pressure.
3.Recommendations for alternative solutions
If a high intensity connection is required, the following methods are recommended:
- Mechanical connection: use riveting, bolt connection or buckle structure to avoid problems in heated areas, suitable for automobile and electronic equipment housing.
- Adhesive+mechanical composite: Combine epoxy resin adhesive with spot welding to balance sealing and strength.

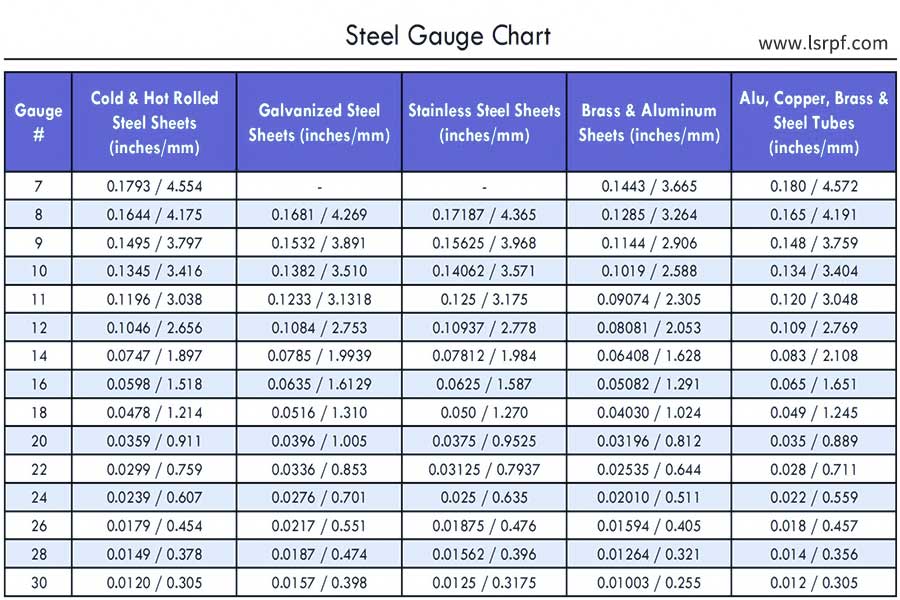
How to select sheet metal thickness based on the sheet metal gauge chart?
1.Clarify application scenarios and functional requirements
Determine the required sheet metal thickness range according to the load bearing requirements, usage environment and assembly method of the member. For example:
- Lightweight components (electronic case): Preference should be given to thin plates (corresponding gauges 20-24, thickness 0.5-0.8mm).
- Structural support (mechanical brace): Medium thick plates (specifications 10-14, thickness 1.0-1.6mm) are required.
2.Match material type and thickness range
The thickness of different materials varies widely, and the mechanical properties need to be selected:
| 재료 유형 | Common thickness range (mm) | Corresponding Gauge Number | Applicable Scenarios |
| 스테인리스 스틸 | 0.5-2.5 | 20-10 | Medical devices, chemical containers. |
| Aluminum plate | 0.4-1.5 | 22-14 | Electronics radiator, automotive lightweighting. |
| Carbon steel | 0.8-3.0 | 18-8 | Electronics radiator, automotive lightweighting. |
| Type of process | Principle of thickness adaptation |
Example of Process Parameters
|
|
| Bending process | Minimum bending radius ≥thickness*2. | Aluminum sheet metal Gauge 18 (1.0mm) requires R ≥2.0mm. | |
| Laser cutting | Thin plates (≤ Gauge 24) were highly accurate (±0.05mm). | Cutting speed 10m/min, power 2,000W. | |
| Welding process | Preheat if thickness is greater than 1.5mm (e.g. stainless steel). | Preheating temperature to 150-200℃. | |
| Tolerance class | Thickness tolerance range (mm) | Cost impact | |
| Precision grade (f) | ±0.05 | Suitable for high precision instruments with high cost. | |
| Ordinary level (m) | ±0.1 | General industrial scenario, best value for money. |