現代の産業システムでは、成形の意味は、製品形式の正確な実現だけでなく、大規模生産の効率サポートとコスト管理能力にも反映されています。 射出成形は、高圧溶融プラスチックを精密な型に注入し、冷却して硬化させることにより、複雑な構造プラスチック成形の迅速な成形です。
材料の選択により、製品の性能が直接決定され、異なる材料の特性(たとえば、温度抵抗、強度、弾力性)は、製品の関数要件とプロセス要件に正確に一致する必要があります。このペーパーは、射出成形材料の分類と選択の原則を体系化し、エンジニアとデザイナーに実用的なガイダンスを提供し、設計プロセスの最適化、生産コストを削減し、グリーン製造の実践を促進することを目的としています。
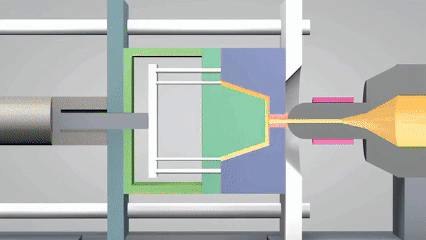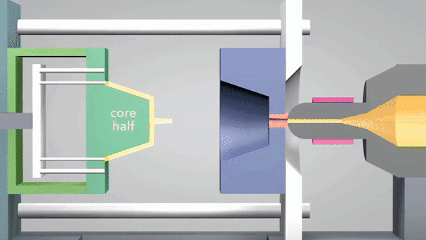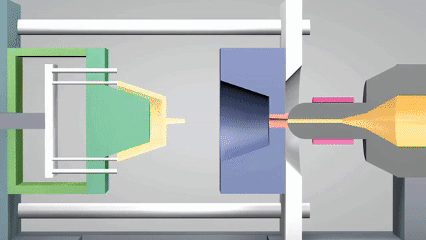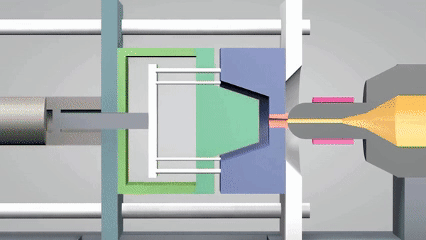
射出成形の定義は何ですか?
プロセスは、複雑な幾何学的構造を正確に複製できるだけでなく、特に電子ケーシングや自動車部品などの工業製品の大規模生産に適した高い生産効率と材料利用の特性も備えています。近年、シリコーン成形は射出型または小さなバッチカスタマイズパーツを生成するために広く使用されています優れた温度抵抗と柔軟性のために、このテクノロジーのアプリケーションシナリオをさらに拡大するために。
射出成形技術の種類は何ですか?
data-pos = "0" data-len = "3" data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 1。 Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> プラスチック射出成形
プラスチック成形のコアプロセスのコアプロセス<粒子、冷却と固化の前に高圧で精密カビの空洞に注入します。
コアテクノロジー:
- 熱流システム:融解の流れパスを最適化することにより、材料の廃棄物を減らし、注入変動効率を改善します。
- マルチキャビティカビの設計:大量の標準化された製品(食料品店、包装容器などなど)に適した多くの部品の最初の金型の生産を実現します。
アプリケーションシナリオ:ペットボトル、文房具、家庭用家電などの一般的なプラスチック製品の大量生産
2。 data-len = "11" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> オーバーモールディング
プラスチックモールディングの分野では、2つの射程モルディングを介した2人プロセス。
テクノロジーの種類:
- 色の射出成形:たとえば、ハンドルの硬いゴム(ABS)とソフトゴム(TPE)を組み合わせて、例えば、スリップ抵抗と美学のバランスを取ります。
- カプセル化モールディング:噴射式成形には、金属フレームの周りにプラスチックを包むための構造(ツールハンドルなど)を強化することが含まれます。
利点:アセンブリステップを削減し、自動車インテリア、家電、その他のフィールドで広く使用されている製品機能と美学の改善。
挿入モールディングは、金属/セラミックインサートを型に備えて金属/span >
キー要素: アプリケーション:自動車電子コネクタ(高温抵抗、プラグおよびプル抵抗)、ホームアプライアンスノブ(金属シャフト+プラスチックシェル)。
data-pos = "0" data-len = "3" data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 4。 data-len = "35" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> プラスチックモールディング用のモールドテクノロジー 金型は注入プロセスのコアキャリアであり、プラスチック成形の精度と効率に直接影響します。
金型設計とタイプ: コアプロセス: 5.Technical選択 プラスチック材料 data-pos = "0" data-len = "3" data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 1。 data-len = "20" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> エンジニアリングプラスチック 2.ジェネラルプラスチック 3. Special Engineering Plastics 金属材料 1。 Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> 金属射出成形材料 2軽量合金 材料 1.カーボン繊維強化プラスチック(CFRP) 2. Glassファイバー強化プラスチック(GFRP) data-pos = "0" data-len = "69" data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 1. biobased材料:pla、pha 2.導電性/熱伝導性プラスチック 1.処理の反復性 熱可塑性物質は加熱すると溶けて流れ、冷却後に固化し、加熱して冷却することができます。 熱可塑性材料は、しばしばより速い結晶化または冷却速度を持っています。 モールディング設計を最適化してエネルギー消費を減らすことにより。 3。 data-len = "26" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> 高次元安定性 absやPCなどの多くの熱可塑性材料は、冷却後に低く制御できるように、プロセス。 4.Diversified material properties Thermoplastic plastics cover a wide range of types from general purpose plastics to high performance plastics such as: This diversity enables plastic molding to adapt flexibly to the functional requirements of different products and further improve performance through modification techniques. 5.Environmental compatibility The recyclability of thermoplastic materials is in line with global environmental trends and reduces the environmental impact of injection molding production production chains. For example, replacing raw materials with recycled plastics (such as rPET) would not only reduce carbon emissions, but would also meet limits on harmful substances imposed by EU regulations such as RoHS. In addition, some thermoplastic materials,such as PLA polylactic acid, are biodegradable and suitable for single-use medical supplies or food packaging, reducing white pollution. 1.Product functional requirements drive material selection Application scenarios: Temperature resistance (e.g. engine components requiring 200 °C heat resistance), bearing capacity (e.g. mechanical parts), sealing performance (e.g. medical catheters), etc. Functional requirements: Electrical conductivity (electronic components), antimicrobial properties (everyday products), transparency (lighting fixtures), etc. JS technology: 2.Matching material performance adaptability Mechanical properties: Tensile strength (e.g. high toughness required for car bumpers), abrasion resistance (e.g. gears). Thermal properties: Temperature resistance range (e.g. PEEK 300 °C), thermal conductivity (e.g. heat dissipation components). Chemical stability: Acid-base resistance (chemical equipment), biocompatibility (medical implants). JS technology: 3.Compatibility guarantee of processing technologies Fluidity: Thin-walled parts require high plastic fluidity (e.g. ABS) and thick-walled parts can be selected for low viscosity PP. Shrinkage control: Precision parts (such as phone frames) require low shrinkage materials (such as POM). Mold lifespan: Corrosive materials such as PVC require chrome molds, while silicone injection molding requires a high temperature resistant coating. JS technology: 4.Balance between costs and mass production efficiency Material costs: The price difference between virgin and recycled plastics. Waste rate: Scrap recycling rate (95% by granulation technology). Production cycle: Rapid prototyping requirements (such as daily orders requiring 72 hours of delivery). JS technology: 5.Environmental compliance requirements Recyclability: Whether the material supports physical/chemical recycling (e.g. PCR recycling of plastics). Limit Hazardous Substances: Follow RoHS, REACH and other regulations (toys must be phthalate-free, for example). Biodegradability: Medical or packaging materials shall conform to EN 13432. JS technology association: 1.Pyrolysis of materials and residual volatile compounds 2.Uneven color and yellowing phenomenon 3.Uncontrolled size shrinkage and deformation 4.Mechanical deterioration 5.Mold thermal damage and shorter service life In the field of injection molding, material selection is the core factor that determines product performance and cost. From basic plastic molding to high performance engineering plastics to special silicone molding, different materials meet the diverse needs of automotive, medical and electronics industries due to their high temperature resistance, strength, elasticity and environmental protection. With increasing environmental regulations, the application of biodegradable plastics (such as plastics) and recycled materials has become a trend, promoting green manufacturing practices. In this process, JS maximizes the potential of injection molding technology through precision die design, intelligent temperature control systems and modification technology. In the future, injection molding will continue to play a key role in lightweight, functionally integrated, and sustainable development as materials science and manufacturing technologies are deeply integrated.
テクニカルタイプ
該当するシナリオ
利点
典型的な素材
プラスチック射出成形
標準化された大量生産。
低コスト、高効率。
abs
オーバーモールディング
機能的統合または外部装飾。
アセンブリが少なく、テクスチャが多い。
pc+tpu、abs+tpe。
挿入モールディング
構造補強または機能統合。
金属とプラスチックの組み合わせ。
Metal Inlay+Pa66。
プラスチック射出型
高精度または複雑な構造コンポーネント
サイズの安定性、長いサービス寿命。
精密電子部品、自動車部品。
射出成形材料の分類は何ですか?
射出成形における熱可塑性の利点は何ですか?
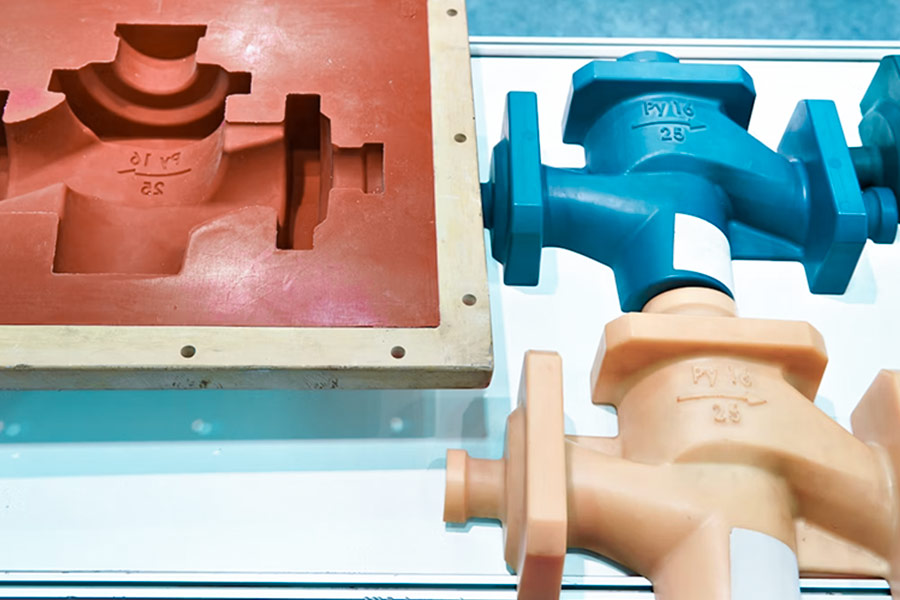
What is the core basis for selecting injection molding materials?
What defects can occur when the temperature of silicone injection molding is too high?

Summary

免責事項
このページの内容は情報目的のみです。サードパーティのサプライヤーまたはメーカーがJushengネットワークを介して提供するパフォーマンスパラメーター、幾何学的許容範囲、特定の設計機能、材料品質と種類または仕上がりがあると推測すべきではありません。これはバイヤーの責任ですこれらの部分の特定の要件を決定するために、パーツの引用を求めてください。
jsは業界をリードする会社ですカスタム製造ソリューションに焦点を当てています。 5,000人以上の顧客にサービスを提供している20年以上の経験により、高精度 cnc machining 、 jsチーム
FAQs
1.What is the difference between plastic and silicone in injection molding?
Plastic (such as ABS) is low-cost, easy to process and suitable for large-scale production. Silicone (LSR) is soft and heat resistant and suitable for soft or medical-grade products such as pacifiers.
2.Are environmental friendly materials widely used in injection molding?
More and more! Biodegradable plastics (PLA) and recycled plastics (rPET), commonly used in packaging and car components, comply with environmental regulations.
3.Does material cost have a big impact on injection molding production?
Material costs directly affect production costs. Reasonable material selection can reduce costs by 30%, but performance and process requirements must be taken into account.
4.How do material properties affect product quality?
The quality of the material properties directly affects the quality of the products. For example, PA has high strength and abrasion resistance, whereas PC is transparent and heat resistant. It is easy to crack, deform or corrode due to Improper material selection, which determines the service life and safety of the product.
Resources