cnc - mit hoher Genauigkeit und Effizienz ist zur Kerntechnologie in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, Automobilherstellung, medizinischen Geräten und anderen Feldern geworden. Egal, ob es sich um eine Präzisionsrotationsformung von Metallteile in der Drehbearbeitung oder eine effiziente Bildung komplexer Oberflächen In der Machen-Maschinen-Verarbeitung. Produkte. Von der Aluminiumlegierung über Edelstahl bis hin zu Kohlefaserverbundwerkstoffen, die Härte, Zähigkeit und thermische Leitfähigkeit jedes Materials beeinflussen die Lebensdauer des Werkzeugs direkt, Schnittparameter und sogar die ultimative Oberflächenqualität.
In diesem Artikel werden die Eigenschaften und die Auswahllogik von Mainstream -Materialien in der CNC -Bearbeitung systematisch analysiert, um den Praktikern von Design bis zur Implementierung umfassende Leitlinien zu geben.
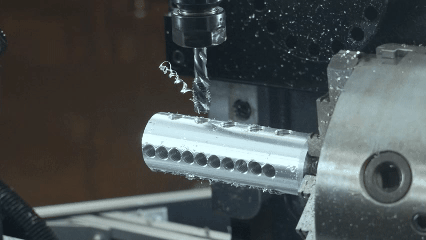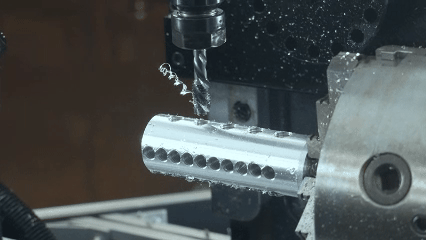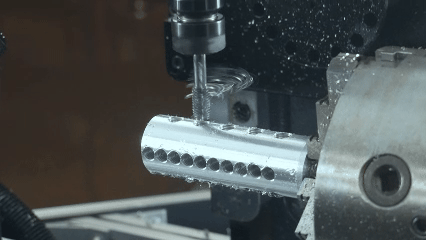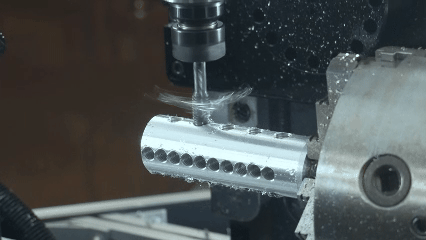
Was ist CNC -Bearbeitung?
Was sind die am häufigsten verwendeten Metallmaterialien in der CNC -Bearbeitung?
In der CNC-Bearbeitung bestimmt die Auswahl von Metallmaterialien direkt die Bearbeitungseffizienz, die Präzision und die Kostenkontrolle des fertigen Produkts. The most commonly used classifications and characteristics of metallic Die Materialien sind wie folgt:
1. Data-Len = "35" Data-V-7b79c893 = ""> Aluminiumlegierung (z. B. 6061, 7075)
Aluminiumlegierung hat die Vorteile des leichten Gewichts, hoher Wärmeleitfähigkeit und ausgezeichneter Schnittleistung und ist das bevorzugte Material für die Bearbeitung cnc cnc IT-LOW-DATE-V-7B79C893 = "" Geeignet für Luft- und Raumfahrtkomponenten wie Klammern und Gehäuse sowie leichte Autoteile wie Räder und Motorhaube. Während der Verarbeitung von THE THE-V-7B79C893 = ""> Während der Verarbeitung von the-7b79c893 = "". Um Oberflächenkratzer zu vermeiden.
2. Data-Len = "35" Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Edelstahl (z. B. 304, 316L)
Edelstahl wird üblicherweise in CNC machining for high corrosion resistance, such as medical devices (surgical instruments), food processing equipment, etc.
3.mold Steel (z. B. S136, P20)
Formstahl wird weit verbreitet In-Stimmabgabe. <">
4.Titaniumlegierung (z. B. Ti6al4v)
Titanlegierung sind zum Kernmaterial von In CNC-machining, specialized tools such as PCD- oder Diamantbeschichtungsschneider -Werkzeuge werden benötigt, und Schneidenparameter (Geschwindigkeit <800 U/min, Vorschubrate <0,1 mm/r) werden optimiert, um das Werkzeug -Ersticken zu hemmen.
5. Copper-Legierungen (z. B. C18150)
Kupferlegierungen haben eine thermische Leitfähigkeit und sind ideal für 5G-HF-Komponenten Kupferkühlkörper. Während der CNC-Bearbeitung muss die Schneidgeschwindigkeit (200-400 m/min) kontrolliert werden
Technischer Punkt: Die Anpassungsfähigkeit verschiedener Metallmaterialien in der CNC-Bearbeitung hängt von der Übereinstimmung physikalischer Eigenschaften und technologischer Parameter ab. In der CNC-Bearbeitung basiert die Klassifizierung nichtmetallischer Materialien hauptsächlich auf ihrer chemischen Zusammensetzung und ihren physikalischen Eigenschaften. Die grundlegende Klassifizierung und Charakteristik von VALLICS-V-7B793 = "> Die Basis-Klassifizierung und -Anscharfsdaten-V-7b79c893 ="> Die Basis-Klassifizierung und die Basisklassifizierung und die Grundnahrungsmittel- und Charakterkennzeichnung von-V-7b791-Materials usw. Folgt: 1. Data-V-7b79c893 = ""> technische Kunststoffe 2. Composite Materials 3. Keramikmaterialien  Was sind die grundlegenden Klassifikationen für die gemeinsame CNC-Bearbeitung nicht-metallischer Materialien?
Was sind die grundlegenden Klassifikationen für die gemeinsame CNC-Bearbeitung nicht-metallischer Materialien?
- Silikon: Hochelastizität, Anti-Aging, verwendet für Versiegelung und medizinische Katheter. Low (500RPM). Material reißen.
- pu (Polyurethan): Abrieb und Tränenresistent, verwendet in Autobodenmatten und industriellen Polsterkomponenten, um die durch hohen Temperatur verursachten Materialverformungen zu vermeiden.
technische Punkt: Die Verarbeitung nicht-metallischer Materialien müssen nach dem Vorgangsparameter nach dem Materialeigenschaften angepasst werden. By using JS's material Datenbank- und Prozesssimulationstools, das beste Verarbeitungsschema kann schnell übereinstimmen.

Wie wählt man CNC -Schneidwerkzeuge und Bearbeitungsparameter basierend auf Materialhärte?
<"> <"> <"> -Kraftungsmerkmale und Verarbeitungsmerkmale von Hardness und Verarbeitungsmerkmalen von Materialien von Materialien von Materialien von Materialien von Materialien von Materials <"
Nach der materiellen Härte (HRC-Rockwell-Härte) gibt es drei Arten von Verarbeitungsobjekten. Unterschiedliche Härte hat unterschiedliche Auswirkungen auf die Werkzeugverschleiß, Schnittkraft und Bearbeitungsgenauigkeit:
| Typische Materialien | Verarbeitungsschwierigkeiten | JS-Technologie-Reaktionsstrategie | |
| Niedrige Härte (HRC <30) | Aluminiumlegierung, Kupferlegierung, Kunststoff. | Akkumulation von Schneiden von Wärme und Oberflächenoxidation. | Optimieren |
| Moderate Härte (HRC 30-50) | Edelstahl, Quench und Temperierte Stahl. | Cutlass- und Werkstückhärten. | Beschichtete Werkzeuge + Staging. |
| Hohe Härte (HRC> 50) | Härter Stahl, Gusseisen, Hardlegierung. | Die Werkzeuge tragen schnell und die Schnittkraft steigt schnell an. | CBN-Schneidwerkzeug+Spezialisierte Fixture-Design. |
-Persparparationsabweichung Die Parameter-Parameter-Parameter-Tabelle Basierend auf der Zusammenfassung der Langzeitpraxis von JS Company werden die folgenden Lösungen in Verbindung mit den Bearbeitungs-Drehszenarien empfohlen:
| Härtequalität | Empfohlenes Werkzeugmaterial | Schneidgeschwindigkeit (m/min) | Futterrate (mm/r) | Schneidtiefe (mm) | JS-Technologie Highlights |
| Niedrige Härte | Beschichtete Hardlegierung (Tialn) | 200-400 | 0.2-0.5 | 1-3 | Multi-Achsen-Bindungskontrolle mit Oberflächenrauheit ≤ 0,8μm. |
| Mittelhärte | Fine Greas | 80-150 | 0.1-0.3 | 0,5-2 | Wärmedeformationskompensationstechnologie mit Genauigkeit ± 0,01 mm. |
| Hohe Härte | CBN-Schneidwerkzeuge (kubische Bornitrid) | 50-120 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.1-0.8 | Spezielle Vorrichtungen können die Vibration verringern und die Lebensdauer dreimal verlängern. |
Technical advantages and practical validations of JS
Werkzeuganpassung:
- Nano-beschichtete Schneidwerkzeuge (wie Tialn, DLC) mit einem Verschleißwiderstand von über 50%.
- Kunden unterstützen, um spezielle Geometrie-Schneidwerkzeuge anzupassen (wie Spiral Blades, Wavy Blades usw.).
Intelligente Optimierung der Prozessparameter:
- Vermeiden Sie automatisch das Risiko einer Tool-Interferenz, indem CAM-Software verwendet wird, um den Schnittvorgang zu simulieren.
- Bearbeitungspflicht adaptiver Futtermittelkontrolle wird angewendet, um die Effizienz um 20%zu verbessern.
Materialdatenbank Unterstützung:
- Es gibt 50 Materialsverarbeitungsparameterbibliotheken (einschließlich Metalle, Kunststoffe und Komposite).
- Echtzeit-Updates zu branchenführenden Materialien wie Hochleistungsschaltkasten wie Pekk und PEI.
Qualitätssicherungssystem:
- CMM full inspection with size tolerance of ±0.005mm.
- Provide cutting parameter verification report to reduce customer trial and error cost.
4.Operational tips and caveats
- Cutting verification: Even if the parameters match, 200mm x 200mm cutouts still need to be processed to test surface quality.
- Tool life monitoring: Cutting force monitoring system (JS system alarm threshold adjustable) for tool wear alarm.
- Environmental control: In the process of processing high hardness materials, the temperature of the workshop (± 2℃) is stable to avoid the hot expansion and cold shrinkage affecting accuracy.

How to solve the tool wear problem of titanium alloy materials in CNC machining?
1.The main causes of wear of titanium alloy tool
- Hardness and work hardening tendency: Titanium alloys (such as Ti-6Al-4V) are prone to work hardening during cutting, resulting in rapid wear and tear tool edges.
- Low heat conductivity: Heat is concentrated in the point of contact of the tool, which exacerbates high temperature softening and chemical wear.
- High chemical activity: Titanium alloy are prone to chemical reactions with tool materials, resulting in adhesive wear (adhesion phenomenon).
2.Targeted solutions and implementation approaches
Combining the technical points of different machining stages, the optimization strategy of JS titanium alloy machining tool wear is introduced below:
| Causes of wear | Solution | Implementation method | Effect evaluation |
| Work Hardening | Use superhard tool materials. | Use cubic boron nitride (CBN) or diamond coated cutting tools with hardness ≥ 40GPa were used. | Knife life is 2-3 times longer. |
| Low thermal conductivity |
Optimization of cooling process. |
High pressure micro lubrication + internal (MQL) + internally cooled cutting tools with coolant pressure ≥ 10MPa. | Reduce cutting temperature by -50%. |
| Chemical bonding wear | Coating technology. | TiAlN/TiCN composite coating thickness of 2-5 μm and friction coefficient <0.3. | The surface roughness ≤ 0.8μm decreased knife viscosity. |
| Unreasonable cutting parameters | Optimization. | Reduce spindle speed (200-400rpm), reduce feed speed (0.05-0.15mm/r) and increase the axial cutting depth (0.5-2mm). | Reduce cutting force fluctuations and improve processing stability. |
| The tool Insufficient geometric design | Improved blade shape and chip removal groove. | Spiral chip groove angles (30-45°) were optimized using large rake angles (15-20°) and negative blade inclination angle (-10-15°). | Smooth chip discharge reduces the risk of secondary cutting. |
3.Comparison of practical application cases
JS optimizes tool and process parameters, and the typical machining effect of titanium alloy is as follows:
| Indicator | Before optimization | JS optimized | Improvement range |
| Tool life (number of pieces) | 50-80 pieces | 150-200 pieces | ↑ 180%-250% |
| Surface roughness (Ra) | 1.6-3.2μm | ≤ 0.8μm | ↓ 50%-75% |
| Processing efficiency (pieces/hour) | 10-15 pieces | 25-30 pieces | ↑ 60%-100% |
| Cutting force (N) | 2,000-2,500 | 1,200-1,600 | ↓ 30%-40% |
4.Precautions and maintenance suggestions
- Periodically inspect tool wear: Changes in blade blade radius change when threshold ≥ 50μm) were monitored using an optical profilometer.
- Avoid the risk of tool breakage: When processing thin-walled parts to reduce feed speed, layered cutting strategy.
- Environmental control: Workshop temperature shall be stable at 20±2 °C and humidity ≤ 50% to prevent moisture absorption deformation of materials.
What are the effects of storage conditions for different materials on CNC machining?
1.Improper humidity control
- Metals (such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys): High humidity can easily lead to oxidation or corrosion of the material's surface, causing burrs or increasing surface roughness during processing. For example, if the oxide layer of aluminum alloy thickens in a humid environment, additional cutting depth or tool replacement is required.
- Engineering plastics (e.g. nylon, PC): After absorbing moisture, the material expands and the stability of the dimensions decreases, which may lead to deformation or size deviation of the processed parts.
2.Effects of temperature fluctuations
- Thermal expansion and shrinkage of sensitive materials (such as titanium alloys and Invar alloys): Temperature changes can lead to changes in material size, which can affect machining accuracy. titanium alloy, for example, expand at high temperatures, leading to tool path deviation during milling and requiring recalibration of machine tool parameters.
- Plastics (e.g. ABS, PEEK): Softens and deforms at high temperatures, increases brittleness at low temperatures, and is prone to cracking or layering during processing.
3.Insufficient packaging protection
- Surface scratches and contamination: If metal sheets are not coated with rust resistant paper or plastic sheeting, scratches during transport or storage can reduce the surface's smoothness and require additional polishing processes.
- Dust absorption: Carbon fiber composites are exposed to dust environments during processing. Impurities can become embedded inside the material and affect the strength of the structure.
4.Lack of anti oxidation measures
- Easily oxidizable metals (e.g. magnesium alloys and copper alloys): If not coated with rust oil or nitrogen protection, oxidation intensifies during processing and tool wear increases by 30%-50%.
- Solution: Use vacuum packaging or desiccant to absorb moisture from the environment and extend the material's shelf life.
5.Misclassification and storage
- Risk of cross-contamination: Mixing hard materials (e.g. tungsten carbide) with soft materials (e.g. polyethylene) may cause scratches on the surface and require separate storage in different areas.
- Physical damage: Excessive pile bar height may cause gravitational bending and affect the clamping stability during lathe machining.
The development trend of future CNC machining materials
1.Accelerate the popularization lightweight materials.
Aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy:
- Continue to replace traditional steel in automotive, aerospace and other fields by optimizing components such as high-strength aluminum alloy, magnesium alloys, and achieve 30%-50% weight loss.
- The improvement of CNC machining processes such as high-speed cutting and micro lubrication has further improved their machining efficiency.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRPs):
- It combines with a metal matrix to form a sandwich structure (such as carbon fiber+aluminum alloy) that balances strength and weight and is widely used in areas such as drones and racing cars.
- CNC machining needs to solve the problems of decolletage and burr, and promote the development of multi-axis coupling and special cutting tools.
2.Surge in demand for high-performance engineering materials
- Titanium alloy and superalloys: core materials used in extreme working conditions such as aviation engines and gas turbines. CNC machining needs to break through the bottleneck of high hardness and low thermal conductivity and promote the upgrading of CBN tool and cooling technology.
- Ceramic based composite materials: For semiconductor equipment and nuclear power components, specialized grinding processes and superhard cutting tools (such as diamond coatings) require to be developed.
3.The rise of sustainable and environmentally friendly materials
- Recycled metal materials: Improve the proportion of aluminum, copper and other metal shavings to be recycled and reused, and reduce the waste of raw materials through CNC netting.
- The biodegradable materials: PLA and PHA in consumer packaging is expanding. CNC machining needs to adapt to its low melting point and good moisture absorption characteristics.
Summary
In the field of CNC machining, material selection and application have always been the key factors to determine product performance and machining efficiency. From traditional aluminum alloys and titanium alloys to emerging carbon fiber composites, CNC machining has diversified the manufacture of precision parts by adapting to the physical properties of different materials. Metallic materials dominate industrial applications due their high strength and thermal conductivity, while non-metallic materials appear in light and extreme environmental scenarios.
In the future, with the increasing demand for lightweight, sustainable, and intelligent CNC machining will further integrate AI-driven material databases, multi-axis coupling processes, and green manufacturing technologies to drive breakthroughs in nano-precision and cross-material integration of machining lathe and machining mill, reshaping the boundaries of manufacturing in the future.

Haftungsausschluss
Der Inhalt dieser Seite dient nur zu informativen Zwecken. Es sollte nicht geschlossen werden, dass die Leistungsparameter, geometrische Toleranzen, spezifische Konstruktionsmerkmale, materielle Qualität und Art oder Verarbeitung, die der Lieferant oder Hersteller von Drittanbietern über das Jusheng-Netzwerk zur Verfügung stellt. Dies liegt in der Verantwortung des Käufers fragen Sie nach einem Zitat für Teile um die spezifischen Anforderungen für diese Teile zu ermitteln.
js ist ein branchenführendes Unternehmen Fokus auf benutzerdefinierte Fertigungslösungen. Mit über 20 Jahren Erfahrung in mehr als 5.000 Kunden konzentrieren wir uns auf eine hohe Präzision cnc maschinen , Fertigung href="https://jsrpm.com/3d-printing">3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing Services. 1.What should be paid attention to when processing plastic parts? When processing plastic parts, cutting speed and feeding force must be reduced to avoid overheating and deformation. Compressed air is recommended for cooling to avoid cracking or discoloration caused by liquid residues. 2.How to determine when to replace CNC tools? See if the color of the chip darkens, if the finish is rough, if there is a noise. If the tool is badly worn, it needs to be replaced to avoid chippings or reduce accuracy. 3.Why is it necessary to clean the material surface before CNC machining? Remove oil stains or impurities from the surface of the material to prevent any impact on accuracy or damage to the tool during processing and to ensure smooth finish and accurate dimensions. 4.What to do if CNC machining aluminum parts is easy to stick to a knife? Use coated cutting tools (such as TiN) to speed up and reduce feed rates and use a highly lubricating coolant to reduce friction and heat accumulation.
JS-Team
Unsere Fabrik ist mit mehr als 100 landwirtschaftlichen 5-Achsen-Bearbeitungszentren ausgestattet und ist ISO 9001: 2015 zertifiziert. Wir bieten Kunden in mehr als 150 Ländern auf der ganzen Welt schnelle, effiziente und qualitativ hochwertige Fertigungslösungen. Egal, ob es sich um eine Produktion oder Massenanpassung mit niedrigem Volumen handelt, wir können Ihre Bedürfnisse innerhalb von 24 Stunden mit der schnellsten Lieferung erfüllen. Wählen Sie JS-Technologie Es bedeutet, Effizienz, Qualität und Professionalität zu wählen. href = "https://jsrpm.com/"> jsrpm.com FAQs
Resources





