Sheet metal fabrication is actually simply the process of taking metal plates and shaping them into the desired shape through a number of different processing methods. The entire process consists of many steps, from first cutting out the overall shape, and then bend sheet metal, and then welding or punching out of certain shapes using molds. Although it may sound somewhat complicated, as long as you have some idea of the basics of how it works, you can customize different metal pieces to your will.
You may ask how we convert a sheet metal into an effective product? The production process from raw material to final product is very interesting, the whole process is like building blocks. In this article, you will get thorough study of the workflow of sheet metal production, and it will allow you to completely understand its working principle, key processes, and precautions.
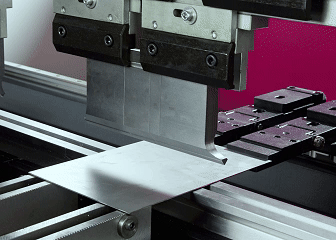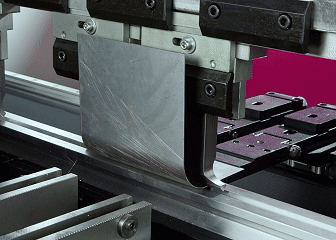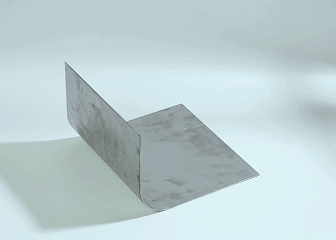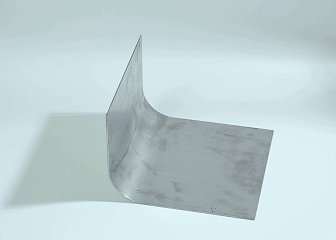
What is sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal processing will be able to turn a sheet metal into the desired components! The process is actually quite simple. You draw up a plan of what you want to do first, make a test piece to try things out, and if everything is fine, use a laser to cut the iron sheet into the shape you want. To proceed to bending sheet metal, the iron sheet is bent into various angles, and the complex pieces need to be joined together by welding.
Aluminum sheet metal and stainless steel are the materials most frequently employed. Aluminum sheet metal is light in weight and rust-resistant, whereas stainless steel is heavy-duty and durable. Galvanized sheet metal also has an excellent cost-performance ratio. With the right material, components will be longer-lasting.
Sheet metal processing is better than conventional methods as far as material efficiency is concerned. It is similar to unfolding an airplane from paper, sheet metal bending directly, and the leftovers can be recycled as well. And the most convenient part of it is that even if you want to manufacture a tailor-made special shape, you do not have to re mold, change the cutting route or set the machine parameters, and the manufacturing can be done on the spot.
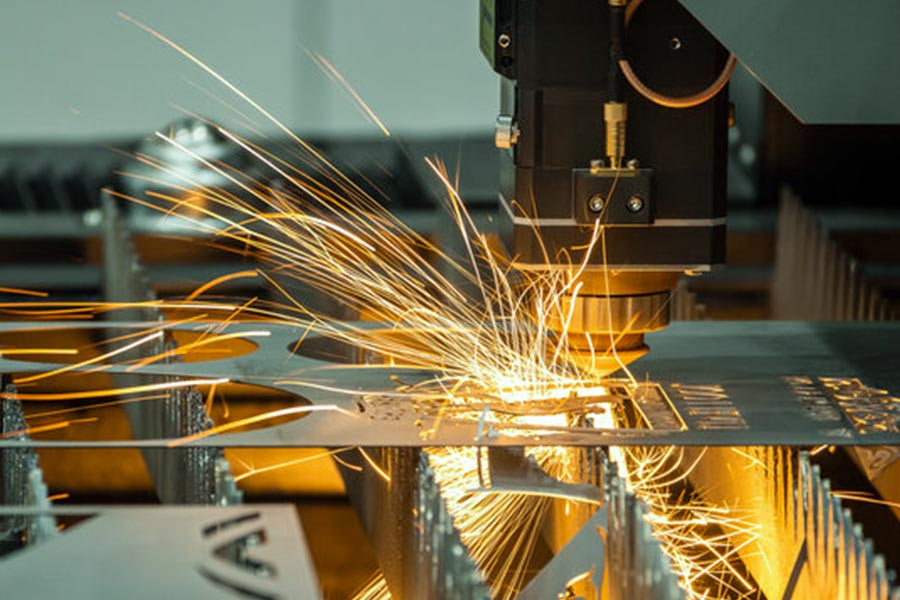

What sheet metal fabrication techniques are commonly used?
1.Cutting and processing stage
Simply put, it means cutting the sheet metal into the desired shape. There are three commonly used cutting methods: laser cutting, water jet cutting, and laser tube cutting. Generally, it can handle plates with a thickness of 0.024 to 0.25 inches, but if customers have special requirements, such as thinner rice cooker liners or thicker engineering components, adjusting the equipment parameters can also be done. The key to this step is to cut it accurately, as all subsequent processes need to be processed according to this shape.
2.Deformation stage
At this stage, it is not necessary to cut open the metal plate, but to deform it through various techniques. There are mainly two methods used:
Sheet metal bending:
Generally, machines are used to fold metal plates into specific angles. Nowadays, bending machines with CNC systems are used. Ours company can generally achieve an accuracy of ±0.1mm, and even the most complex shapes can be repeatedly made. Like the common shelf racks and equipment casings, they are basically folded out like this. Both thin aluminum plates and thick steel plates can be processed, and steel structures on construction sites and automotive chassis components cannot do without this technology.
Stamping forming:
This operation is similar to stamping with a mold and pressing the metal plate into a concave convex shape at once. The metal connectors in car doors and mobile phones are all stamped out. The biggest advantage is fast speed, especially suitable for mass production, such as, making car parts can produce hundreds of them in a few minutes. It is also possible to perform special treatments such as embossing and curling, which are both practical and aesthetically pleasing. From thin iron sheets to thick steel plates, they can be punched and used in many industries.
3.Assembly and welding
The various parts are assembled and fixed mainly by two welding methods:
- TIG welding: Slowly welding with argon gas protection, suitable for welding thin plates or fine parts, such as stainless steel countertop joints that need to be aesthetically pleasing.
- MIG welding: Using mixed gas protection, welding quickly and firmly, suitable for welding thick steel plate structural components.
- For example, when it comes to motorcycle splash guards, which require both solidity and waterproofing, experienced technicians often choose TIG welding to ensure quality.
What is the process of sheet metal fabrication?
Phase 1: Design and material preparation
This is the first step in sheet metal processing, and this stage directly determines whether the subsequent processing can proceed smoothly. Our experienced engineers will first select suitable materials according to the product usage scenario. For example, rust-free aluminum alloy is often used for washing machine shells, and carbon steel plates with good load-bearing properties are often used for factory equipment brackets.
Then use 3D design software to draw detailed drawings, focusing on key parameters such as the angle value of the bending position and the size of the opening. These data are like construction guidelines for the processing link.
Our technical team pays special attention to detail control in this link. For example, when encountering thin plates below 0.8 mm, additional anti-deformation support points will be marked on the drawings, which can effectively reduce the number of later debugging and help customers save time and cost.
Phase 2: Precision cutting and surface pretreatment
Choose the cutting process depending on the thickness of the material and ease of shape:
- Laser cutting is appropriate for plates 1-12mm thick and can preserve the cut smooth.
- Water jet cutting is used for cutting thin plates with simple deformation.
- Shearing by conventional methods is used in rapid cutting of linear profiles.
When cutting, sandblasting will have to be done to remove the oxide film and oil marks like "waxing the face" from the metal, which is critical to the quality of the subsequent spraying or welding.
Phase 3: Forming and quality control
The flat plate is processed into a three-dimensional component by a bending machine or a stamping die. When operating, pay attention to the following:
- Thick plates over 3mm need to be bent in stages to avoid stress concentration.
- The arc part adopts progressive forming, and the deformation does not exceed 15° each time.
- After the modeling is completed, the magnetic polishing machine is used to remove the burrs, and the hole spacing and the flatness of the assembly surface are checked. Parts with an error of more than 0.2mm must be reworked.
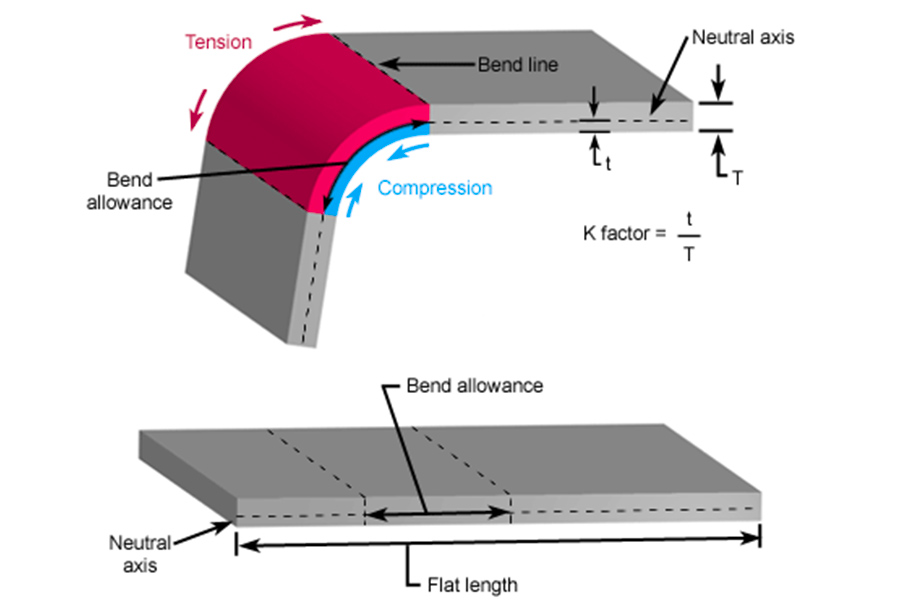
The bending rebound compensation database independently developed by JS can ensure the sheet metal bending tolerance of ±0.005mm.
In the whole process, the design drawings are compared with the physical samples at least three times: check the size after the initial cutting, monitor the deformation in the forming stage, and do the overall adaptation test before the final assembly. This interlocking control method can effectively avoid material waste and later repairs.
How to choose materials for sheet metal fabrication?
1.Define the conditions of use
- Environmental conditions: For example, stainless steel or aluminum plates are to be selected in contact with corrosive liquids, and heat-resistant steel is to be considered in high-temperature environments.
- Stress conditions: Thick carbon steel plates are to be selected for load bearing, and aluminum alloys are more suitable for light scenarios.
2.Compare material properties
Here is a comparison table for more clarity:
| Material type | Advantage | Disadvantage | Typical uses |
| Stainless steel | Good rust resistance and easy to clean. | High price and difficult processing. | Kitchen equipment, medical supplies. |
| Aluminum alloy | Lightweight and rust free. |
The strength is inferior to steel.
|
Automotive components, decorative panels. |
| Plain carbon steel | Cheap and easy to process. | Easy to rust. | Building structure, mechanical base. |
| Copper alloy | Good conductivity and beautiful appearance. | Expensive price, soft. | Electrical components, decorative surface layer. |
3.Consider processing requirements
- Select materials with good ductility (such as aluminum plates) for sheet metal bend forms.
- Pay attention to the hardness of the material for complex cutting. Too much hardness will increase tool loss.
4.Consider the economy
- Mass production considers the unit price of the material first, and small-scale customization considers the processing cost. For example, although stainless steel is expensive, it saves the cost of rust prevention treatment, and the overall price may be more economical.
- Note taking 10-15% performance margin, and never choose the material at limit value exactly, which is safer and durable.
What tools are crucial for sheet metal fabrication?
1.Cutting tools
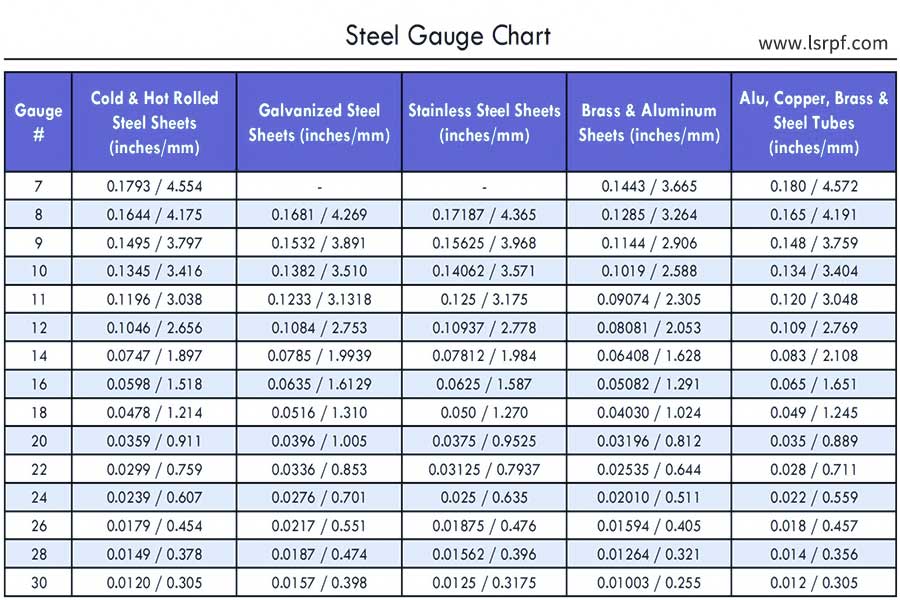
- Laser cutting machine: Mainly used for thin plates below 6mm, with an accuracy of 0.02 mm. It is best to refer to the sheet metal gauge chart when adjusting the power.
- CNC punching machine: Suitable for medium and thick plates of 1-8mm, the punching spacing should be at least 1.2 times the plate thickness to prevent edge cracking.
- Water jet cutting machine: Best for thick plates above 8mm, the cutting speed should be adjusted according to the thickness, and it is easy to cut crooked if it is too fast.
2.Bending and shaping tools
- The opening angle of the bending machine mold must follow the plate thickness: for example, 88-degree mold is used for 1.5 mm aluminum plate, and 120 degrees or more is required for thick steel plate.
- When using a rounding machine, thin plates should be rolled slowly for several more turns, while thick plates need to increase pressure to form at one time.
3.Welding and connection equipment
- When the argon arc welding machine welds thin plates below 3mm, the current should be controlled between 50-150 amperes, otherwise it is easy to burn through.
- Laser welding machines are suitable for precision parts. The focus position should be fine-tuned according to the sheet metal gauge chart. If the deviation exceeds 0.5mm, the welding will not be strong.
- Pressure value of the riveting machine: 3mm stainless steel plate requires at least 8 tons of pressure, and 3 tons is enough for thin aluminum plate.
4.Auxiliary measurement tools
Three items must be prepared: digital caliper (accuracy to 0.01mm), R angle gauge (measure bending arc), plate thickness micrometer. Every time the material batch is changed, the actual thickness must be re-measured. The market plate often has an error of ±0.1mm, which will cause the bending angle to deviate by more than 2 degrees.
What do sheet metal fabricators do?
Metal sheet fabricators play multiple roles in the industry chain. They must understand materials and master manufacturing processes. They mainly undertake work at four levels:
1.Material bridge role
First, they must be a good "raw material steward". They must connect with material factories to ensure a stable supply of sheets and select materials according to the needs of downstream industries such as automobiles and home appliances. For example, medical equipment must use medical-grade stainless steel, and communication base stations must choose corrosion-resistant galvanized sheet metal.
2.Technology conversion
They actually convert the CAD drawings provided by customers into process flows that can be actually produced. There are many technical contradictions that need to be resolved here. For example, the product must be beautiful in shape and must not crack when bent. At this time, the thickness of the sheet must be adjusted or a material with better ductility must be used.
3.Provide customized services
Facing different industries, we have to show our unique skills. When we make covers for automobile companies, we must ensure a surface accuracy of 0.1 mm, and when we make server cabinets, we must consider the layout of heat dissipation holes. JS provides a full-process service from proofing to mass production, and can also accept small batch customization.
4.Quality control
We start from the incoming inspection, checking the thickness tolerance and surface quality of each batch of plates just like a currency detector checks banknotes. The production process is even stricter. Our quality inspectors will stop any bending angle error exceeding half a degree or pores at the welding point. They also have to keep an eye on the update of industry standards, such as the latest environmental protection requirements must be implemented in the production process in a timely manner.
Why invest in sheet metal fabrication for your project?
Choosing professional sheet metal fabrication services can bring three core values to the project, and these advantages are particularly evident in actual production:
1.Double guarantee of precision and efficiency
Modern processing equipment is like a precision scalpel. CNC laser cutting can control the error within ±0.005mm, and we can reduce rework by 90%.
With automatic bending machines and welding robots, our regular orders can basically be completed within 1-2 weeks, and the JS project cycle is shortened by an average of 15%. This processing capability is particularly suitable for precision parts that require a perfect fit, such as the metal shell of medical equipment or the bracket structure of precision instruments.
2.Full process risk control
Starting from the design stage, we started to intervene in optimization. Our engineers suggested changing the right-angle bend to a design with a circular arc, which not only improves the strength but also avoids the risk of cracking.
There are also particularities in material selection. For example, outdoor parts will recommend galvanized steel metal instead of ordinary steel plates. Although it is 15% more expensive, its service life can be extended by 3 times. This early optimization can reduce 80% of assembly problems in the later stage.
3.Compliance and cost balance
We have passed ISO certification and established a complete traceability system. The source batch and processing records of each plate can be checked. A medical device manufacturer we recently cooperated with reduced the product defect rate to less than 0.02% through this control.
In terms of cost control, the intelligent nesting system can maximize the use of materials like a jigsaw puzzle, and the scraps are reduced by 20% compared with the traditional method, which can save considerable costs for mass production.
Summary
Sheet metal fabrication is a systematic process of processing metal sheets into precision parts. The core of this technology lies in precise control of processing parameters, such as adjusting the mold gap of the bending machine according to the thickness of the sheet, and using laser cutting equipment to ensure a smooth cut.
Through this precise control, the size error of the finished product can be controlled within the range of hair thickness, meeting the precision requirements of fields such as automotive parts and medical instruments.
Modern sheet metal processing not only pursues precision, but also pays more attention to environmentally friendly production. Especially for some leading companies, JS with years of accumulated process databases, can ensure a product qualification rate of over 98% and achieve fast delivery, helping customers launch new products faster.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What is the role of sheet metal molds?
Sheet metal molds are used to stamp, form or cut metal sheets. External force is applied by a press to quickly deform or separate the material according to the shape of the mold, achieving efficient processing of holes, bends or complex contours, ensuring dimensional consistency and process stability during mass production.
2.How to choose the thickness of sheet metal materials?
The thickness of sheet metal materials should be selected based on the application scenario, load requirements and processing technology. Structural parts should meet the strength requirements and choose thicker plates, while decorative parts can be thinner. When bending or stamping, the equipment capacity should be matched to avoid cracking or deformation. At the same time, balance the cost, avoid excessive redundancy, and refer to industry standards or design specifications.
3.What is the difference between sheet metal and casting?
Sheet metal is formed into plates (such as steel and aluminum) through cold processing such as cutting and bending, which is suitable for thin-walled and lightweight structural parts. Casting is to inject molten metal into a mold for solidification, which is suitable for complex shapes and thick-walled parts. The material utilization rate is low, but high-precision parts can be mass-produced.
4.What is the principle of laser cutting?
Laser cutting uses a focused high-energy laser beam to irradiate the material, causing it to melt, gasify or reach the ignition point quickly, and at the same time uses high-pressure gas (such as oxygen and nitrogen) to blow away the slag to form a precise incision. The movement of the laser head is controlled by a CNC system to achieve complex shape cutting, which is suitable for metal and non-metal plates.